In our last episode (… a few months ago 😓) Xuan-zang met the Qaghan of the Western Turkic Khaganate, and made a good impression, allowing him to travel safely further south and westward toward the city of Samarkand.

If you need to brush up on earlier episodes, click below:
- Prologue
- Part 1 – Northern Silk Road
- Part 2 – Over the Tian Shan mountains
- Part 3 – Western Khaganate
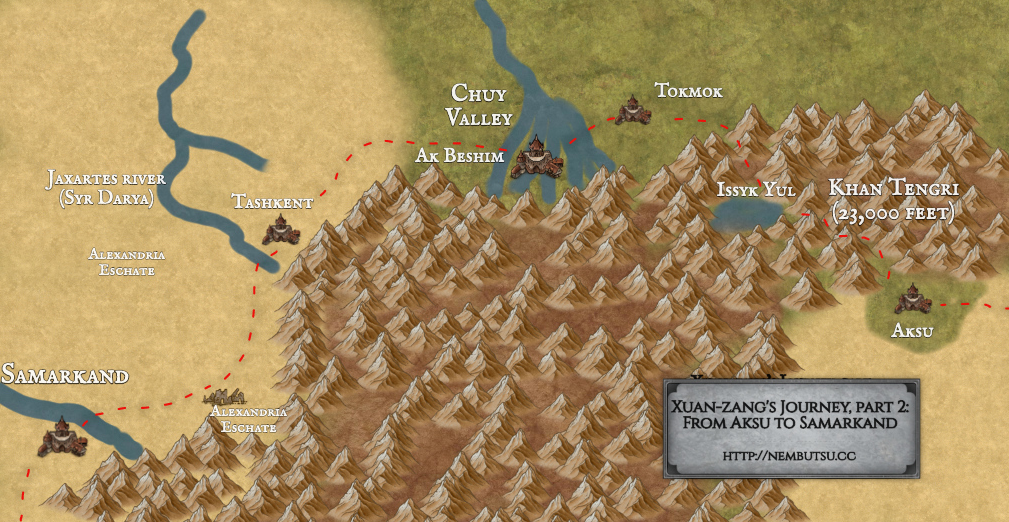
Samarkand
Samarkand is a fascinating place: a fabulously old city, and a major hub on the Silk Road. All the way back in the time of Alexander the Great’s conquests in 329 BCE, 1,000 years before Xuan-Zang, the city was called Marakanda (Μαράκανδα) in Greek and was part of the Achaemenid Persian Empire before that. By Xuan-zang’s time the city was part of the Sassanian Persian empire, and still a major trading hub, known even to the Chinese, but I was unable to find a reliable source on the Chinese name at the time. Modern term is 撒马尔干 (sǎ mǎ ěr gàn ?). The city at this time was almost entirely populated by Sogdian Iranian people, whom we’ve also seen in past episodes. This far west from China, Xuan-Zang probably saw very few if any Chinese people, and instead encountered many people from other cultures and parts of the world. He was very much a “stranger in a strange land”.1
However, because this city was part of the Sassanian Empire, the official religion was Zoroastrianism, not Buddhism, and as Xuan-zang came to the city, he noticed that the Buddhist monasteries there were abandoned and neglected. Some of Xuan-zang’s followers went to pay their respects at these monasteries, but they were chased off by a mob of Zoroastrian followers with flaming brands. Later, the king heard what happened and arrested the mob leaders and was going to pass sentence to mutilate them. Xuan-zang begged for leniency, and so they were flogged and expelled from the city.
The king of Samarkand wasn’t particularly friendly to Xuan-zang, but their relations did improve. Further, it seems that later the king of Samarkand made friendly, diplomatic overtures to Tang-Dynasty China as a foil to the Western Turkic Khaganate, but these did not go very far. Decades later, Great Tang’s expansion reached all the way to Samarkand and they briefly ruled for a few decades until the Battle of Talas later. All this happened decades after Xuan-zang visited the city though.
In any case, Xuan-zang wisely did not stay long in the city and turned at least to towards the south.
Heading South
Up until now, Xuan-zang’s journey from the Yumen Pass in China to Samarkand, over the Tian Shan mountains and across two deserts, has mostly been a westerly journey. But this was as far west as Xuan-zang would go. The road to India was now in a south-southeasterly direction passing through places like modern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan. These areas were not part of Sassanian Empire, and instead were local princes and minor rulers with complicated relations with regional powers. These areas were more Buddhist-friendly as well due to the legacy of Bactrian Greeks,2 but more importantly due to the Kushans who came later. Much of these lands were former Kushan territory, and their good governance and patronage of Buddhism at the time allowed things to flourish on the Silk Road.
The first obstacle Xuan-Zang and his party ran into was the famous “Iron Gates“.

Because this area was a choke-point for travel, it was often garrisoned, and he described “double wooden doors, strengthened with iron and furnished with bells”. In any case, Xuan-zang seemed able to pass through without much issue.
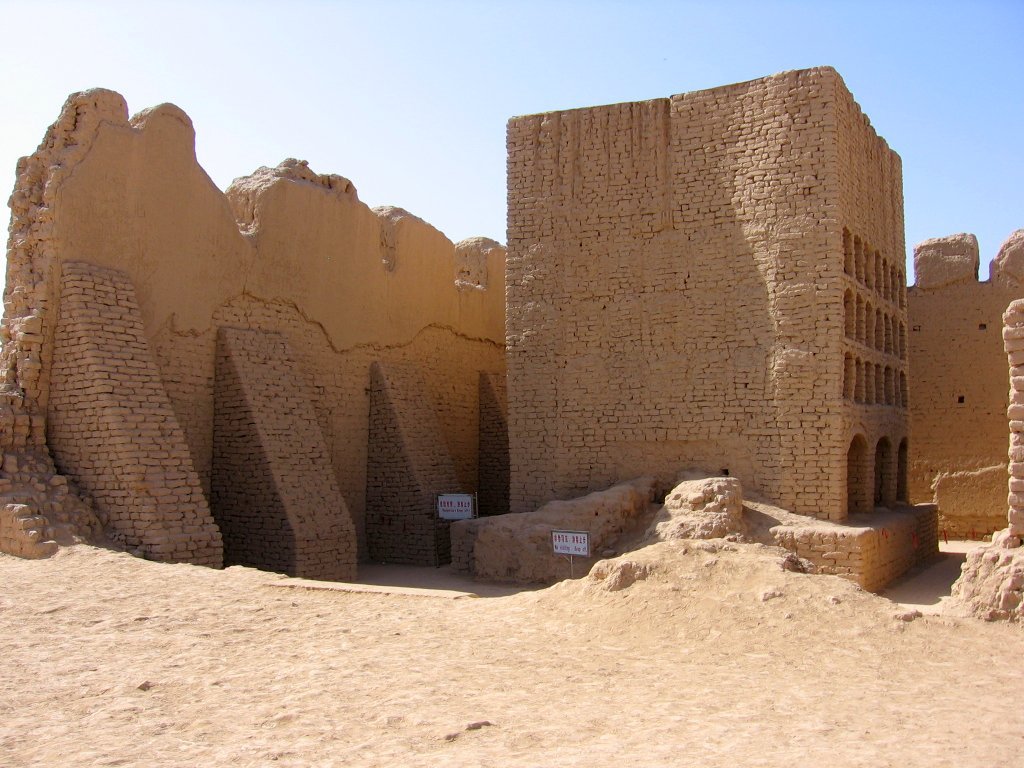
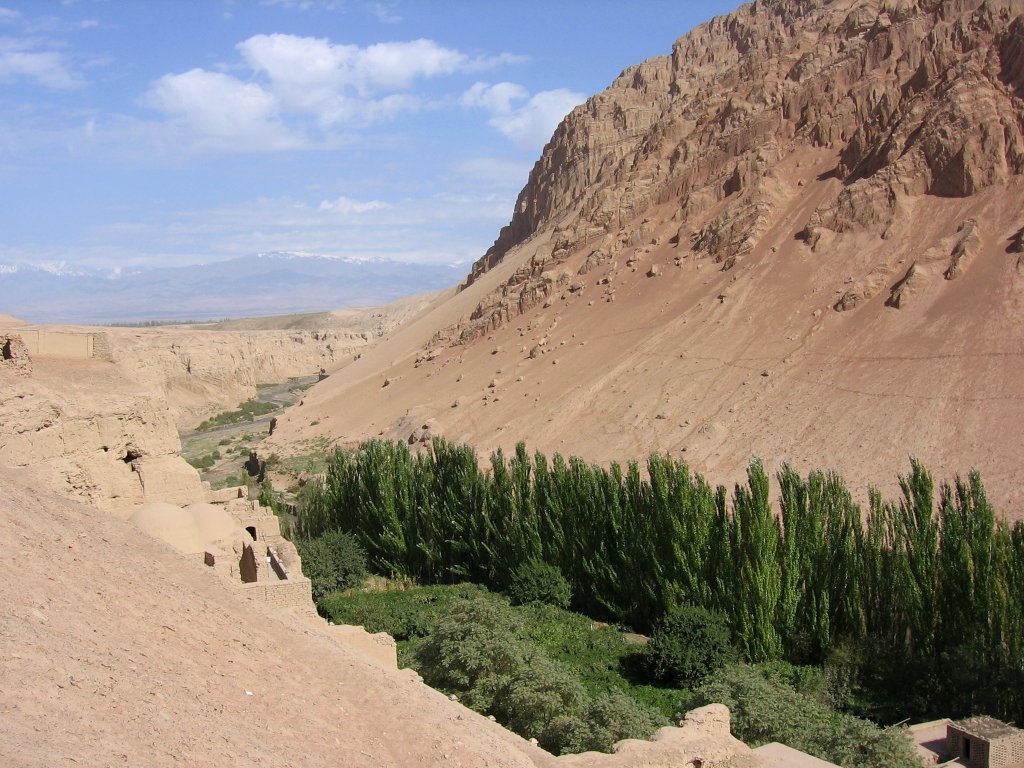
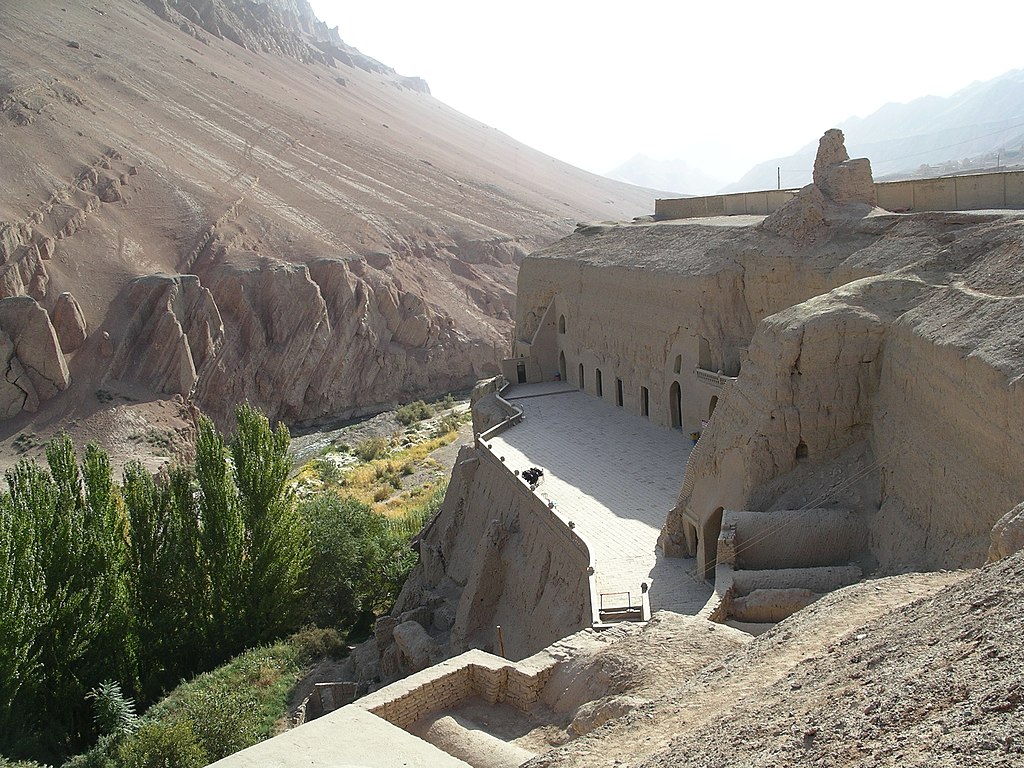
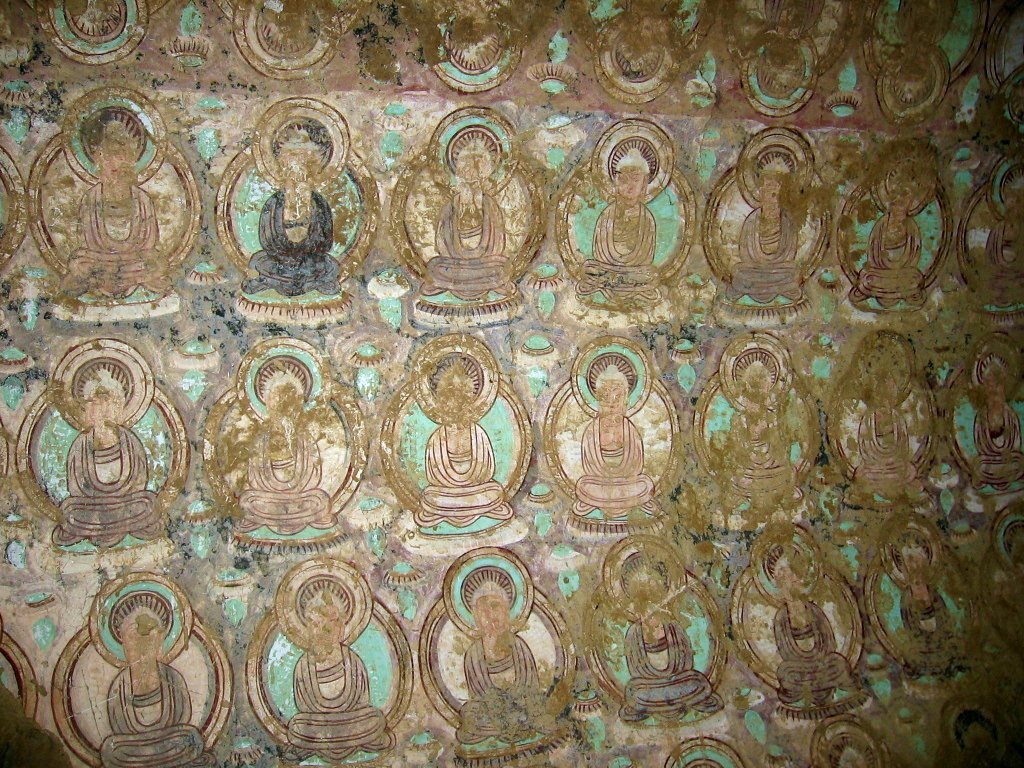
After crossing the Oxus River (now the Amu Darya), he returned to regions where Buddhism was still flourishing namely in the small city of Termez. Termez was once a major city of the Kushan Empire, but was much more diminished by the time Xuan-zang arrived. The Buddhist community here numbered about 1,000 monks. It was here that he saw the Ajina Tepe monastery and its excellent works of art.
In fact, from here Xuan-zang would behold some pretty amazing spectacles. Many people may not realize that the lands we now call Afghanistan were once bastions of Buddhism along the Silk Road, and boasted many treasures, monasteries, and a very eclectic culture.
But first, Xuan-zang had to deal with a series of problems in the city of Kunduz.
Intrigue and Murder at Kunduz

Xuan-zang’s visit to the city of Kunduz was no accident. After meeting the king of Turfan way back in episode one, and the Qaghan of the Western Turks in episode three, he had many letters of introduction to the Prince of Kunduz named Tardu. As rulers on the Silk Road, they were all related by family or marriage, so Xuan-zang had little trouble getting an audience with Prince Tardu.
Except for one problem: the Prince’s wife had recently died, and he was in mourning. Later, Tardu abruptly married another daughter of the king of Turfan (episode one), and she in turn plotted with his son from the first marriage. This is starting to sound like the plot of a historical K-drama, doesn’t it?
Before long, Prince Tardu was poisoned and died. The new queen married the prince, and ruled Kunduz thereafter.
Xuan-zang did his best to lay low, and stay out of the issue. His delays at Kunduz meant that he had time to get to know another Buddhist monk named Dharmasimha. Dharmasimha and Xuan-zang debated Buddhist thought and treatises for some time, but Xuan-zang felt Dharmasimha didn’t know as much as he was hyped up to. Dharmasimha for his part, acknowledged his shortcomings, and tried to stay humble about it.
Moving On
Before Prince Tardu’s death, he had encouraged Xuan-zang to visit another city named Balkh, also in modern Afghanistan. Balkh had quite a few sites to see, and since some Buddhist monks were already planning to head back there, Xuan-zang accompanied them. After passing through a city named Tashkurghan (modern Kholm, not related to a similar city in China), they reached the verdant lands of Balkh.
The city of Balkh, known to the Greeks of Alexander the Great as Baktra (Βάκτρα) and Baítíguó (白題國) in Chinese to Tang-dynasty China, was important since very far back in antiquity. Balkh was the traditional birthplace of the Zoroastrian religion, and an important cultural center to Persian people since very ancient times, rivaling cities further to the west such as Babylon and Ecbatana in importance. According to Buddhist tradition, the first two of the Buddha’s disciples also hailed from Balkh, and made the first stupa. Centuries later, it was here that Alexander had married a bride named Roxana, seeking to unify western Greek culture with the eastern Persian culture. Later in the Hellenstic Age, it was an important center of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom.
Needless to say, while few people have heard of Balkh today, it was a very important city across many centuries.
During Xuan-zang’s time, the lands around Balkh were still very fertile (desertification happened gradually later). Even with the widespread destruction the Hephthalities (a.k.a. “white huns”), the lands were still prosperous, if somewhat depopulated. There were two major monasteries in the area collectively known as the Nava Vihara, that belonged to the Sarvastivadin tradition of “Hinayana” (early Indian) Buddhism.3 There were tens of thousands of monks in attendance, and Balkh was one fo the remaining places where teachers were regularly installed from India. Similar to Bamiyan, the Naha Vihara boasted massive statues of the Buddha as well. Interestingly, even as far as the 8th century, long after Xuan-zang was dead, an Arab historian named Umar ibn al-Azraq al-Kermani recorded a place of worship here similar to the Kabaa in Mecca. But instead a Buddhist stupa was enshrined inside, with a cloth draped over it, in accordance with Persian custom of showing veneration.
Xuan-zang stayed at the Nava Vihara for a month, and became good friends with a monk there named Prajnakara. Xuan-zang seemed to finally find a monk of high-caliber, who had a good depth of understanding of Buddhist doctrine, even if he was a “Hinayana”, not Mahayana Buddhist. The two journeyed together further south to Bamiyan.
In our next episode, we’ll explore Xuan-zang’s visit to the great Buddha status of Bamiyan, and Xuan-zang is reaching the borders of India. But first, he has to cross the Himalayas…
2 A few articles on the Gandharan culture, and the cultural connections between the Bactrian Greeks and Buddhism.
3 Although the Sarvastivada school was not Mahayana Buddhism, Mahayana Buddhism inherited a lot from it anyway: canon of texts, certain viewpoints, etc. Another important early school that influence Mahayana were the Dharmaguptaka, who mostly gave their monastic traditions and rules to the Mahayana.






























You must be logged in to post a comment.